Educational Video
Employees and Contractors are common ways that businesses get work done. While they are often referred to by their tax status, W-2 Employees vs 1099 Contractors, labor law governs them very differently. Contractors are much more flexible, but traditional employees are often more reliable in crunch times.
W-2 Employees
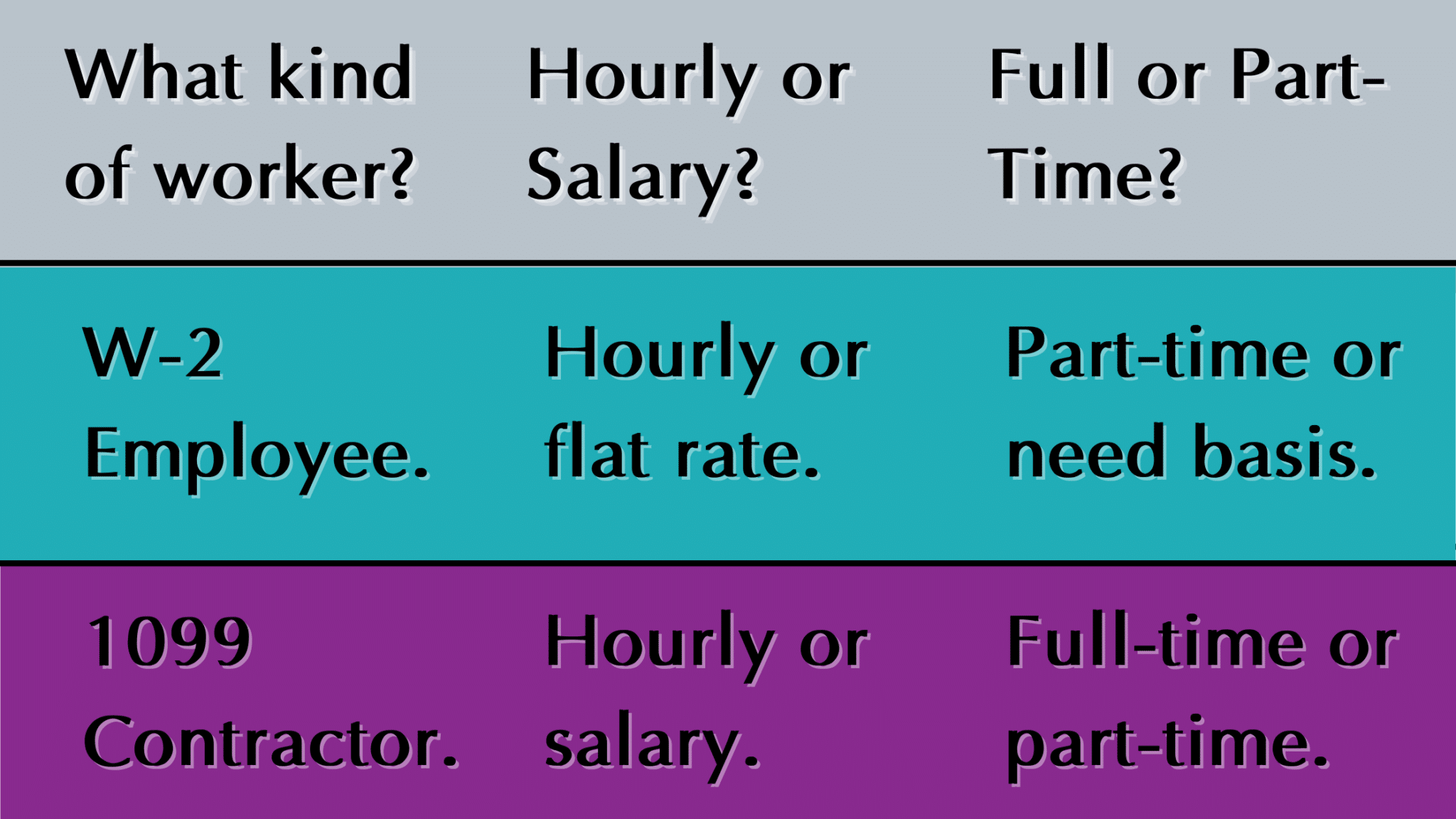
A W-2 employee is a typical employee that works for you either part-time or full-time. With W-2 employees, you must withhold payroll taxes from their paychecks, and your business pays the payroll taxes on their earnings. The W-2 employee can be either hourly or salaried. When it comes to labor laws, such as minimum wage and overtime, W-2 employees are protected. It is often easier to hire W-2 employees, as most workers want full time work. You can also control the schedule of traditional employees, although this is governed by labor law. The W-2 employee will be more reliable since they usually work for you full time with a set schedule and understand the company’s culture. The cons are, of course, they cost more in payroll taxes and benefits, and you have a lot of labor laws to follow.
1099 Contractors
A 1099 worker usually works for you part-time. When it comes to payroll taxes for 1099 workers, your business doesn’t need to withhold taxes or pay taxes on their earnings, the contractor is treated as another entity that is responsible for their own self employment taxes and income taxes. The contractor is never salaried and is less protected by labor laws. The pros of working with 1099 workers are fewer costs because you don’t have to pay payroll taxes for them, you don’t have to pay workers compensation insurance or provide benefits like healthcare, and – because your business is not subject to the same labor laws that apply to W-2 employee’s- you’re less likely to be sued on the grounds of labor law violations. A contractor also makes for a more casual relationship between your business and the individual, so there is more flexibility.
Which Classification Makes More Sense?
If you misclassify an employee as a contractor, it can lead to audits, penalties and fees, so we want to avoid that at all costs. The most important factors of the determination are the level of control exercised by the hiring party. There are three areas the IRS looks at to make this determination- behavioral control, financial control, and the relationship. Both types of workers can be a great fit for your business depending on what you need them for. Just DON’T you accidentally file one as the other because the IRS will fine you with penalty and fees.








