Tax avoidance strategies can legally reduce your tax burden when implemented correctly. The IRS collected $4.9 trillion in 2023, yet many taxpayers overpay due to poor planning.
We at Bette Hochberger, CPA, CGMA see clients save thousands annually through compliant tax strategies. The key lies in understanding legal boundaries and avoiding audit triggers.
What Makes Tax Avoidance Legal While Tax Evasion Is Criminal?
Tax avoidance uses legal methods to reduce your tax burden, while tax evasion means you intentionally hide income or fabricate deductions to avoid taxes. The IRS defines tax evasion under IRC Section 7201 as the voluntary, intentional violation of a known legal duty that can result in up to five years in prison and fines that exceed $100,000. Legal tax avoidance includes maximized deductions like the Qualified Business Income deduction worth up to 20% of qualified business income, contributions to retirement accounts, and strategic income timing.

Tax evasion activities include underreported cash income, false business expense claims, failure to report foreign accounts that exceed $10,000, and maintenance of two sets of books.
IRS Enforcement Patterns Reveal Clear Legal Boundaries
The IRS flags specific behaviors that cross from legal avoidance into criminal evasion. Cash-intensive businesses face heightened scrutiny when lifestyle doesn’t match reported income levels. Inconsistent tax return filings or skipped years trigger audit patterns that can escalate to criminal investigations. The agency uses third-party reports to detect discrepancies between reported income and actual financial activity. Industries like restaurants and gig economy roles receive particular attention for unreported cash transactions.
Documentation Standards Separate Legal Strategies From Criminal Activity
Legitimate tax plans require thorough record-keeping with verifiable receipts and income logs. The IRS examines the substance over form of transactions, which means disguised expenses or income arrangements will face challenges regardless of paperwork. Honest mathematical errors typically result in civil penalties rather than criminal charges, while intentional document falsification constitutes fraud. Consistent, accurate records with clear business purposes protect against criminal liability while they support aggressive but legal tax positions.
Common Legal Avoidance Methods Pass IRS Review
Business owners can deduct various expenses including office supplies, travel costs, and home office expenses to reduce taxable income. Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) allow tax-free withdrawals for qualified medical expenses, with pre-tax contributions that reduce taxable income. Charitable donations to registered organizations provide tax receipts that help lower taxable income significantly. The Child Tax Credit provides parents with up to $2,000 per qualified child, which impacts overall tax liability substantially. These strategies demonstrate how proper planning creates substantial tax savings while you maintain full compliance with federal requirements.
Strategic Tax Planning Methods That Pass IRS Scrutiny
Business Structure Selection Reduces Tax Burden
Pass-through entities like S-corporations and LLCs offer significant tax advantages over traditional C-corporations for most small businesses. S-corp owners can reduce self-employment taxes by splitting income between salary and distributions, with only the salary portion subject to the 15.3% self-employment tax rate. An S-corp owner who earns $100,000 might pay themselves a $60,000 salary and take $40,000 in distributions, which saves approximately $6,120 annually in self-employment taxes compared to sole proprietorship status. LLCs provide operational flexibility while they maintain pass-through taxation, though owners must pay self-employment tax on all earnings unless they elect S-corp status.
Income and Deduction Timing Controls Tax Brackets
Cash-method taxpayers can accelerate deductions into high-income years and defer income to lower-bracket periods through careful timing strategies. December equipment purchases, prepaid business expenses, and accelerated depreciation can shift substantial deductions into the current tax year when businesses need them most. Conversely, delayed year-end invoices or postponed asset sales can push income into the following year when tax rates may be lower. Health Savings Account contributions of up to $4,300 for individuals (or $8,550 for families in 2024) provide triple tax advantages with deductible contributions, tax-free growth, and tax-free qualified withdrawals.
Retirement Account Contributions Create Long-Term Tax Shelter
Traditional 401k contributions reduce current taxable income by up to $23,000 for 2024, with an additional $7,500 catch-up contribution for those over 50. SEP-IRAs allow business owners to contribute up to 25% of compensation or $69,000, whichever is less, which makes them powerful tools for high earners. Solo 401k plans permit both employee and employer contributions, potentially allowing total deferrals of $69,000 plus catch-up contributions. These strategies work best when combined with Roth conversions during low-income years to balance current deductions with future tax-free income.
However, aggressive tax positions require careful documentation and professional guidance to avoid audit triggers that can transform legal strategies into compliance nightmares.
What Documentation Prevents Audit Triggers
Meticulous Record-Keeping Standards Stop IRS Challenges
The IRS requires contemporaneous documentation for every deduction claim. Records must exist at the time expenses occur rather than be reconstructed later. Business meal deductions need receipts that show date, amount, business purpose, and attendees – any missing element disqualifies the entire deduction.

Home office deductions require detailed floor plans, utility bills, and exclusive business use documentation since mixed-use spaces face automatic disallowance. Vehicle expense claims need mileage logs with dates, destinations, business purposes, and odometer readings maintained daily rather than estimated quarterly. Cash transactions over $10,000 require Form 8300 filing within 15 days, so cash-heavy businesses must document legitimate sources for every large deposit to avoid money laundering suspicions.
High-Risk Deduction Categories Draw Automatic Scrutiny
Schedule C business losses that exceed three years in five consecutive years trigger hobby loss examinations under IRC Section 183, where the IRS presumes profit motive doesn’t exist. Charitable donations that exceed 50% of adjusted gross income face heightened review, particularly non-cash contributions over $5,000 that require qualified appraisals. Home office deductions claimed by employees were eliminated in 2018, yet thousands still claim them illegally each year. Entertainment expenses became 100% non-deductible in 2022, though many taxpayers continue to claim business meals as entertainment. Travel expenses that mix business and personal activities need precise allocation – the IRS disallows entire trips when documentation shows primarily personal purposes.
Foreign Account Compliance Prevents Criminal Penalties
Form 8938 requires reporting specified foreign financial assets for taxable years starting after March 18, 2010. FBAR filings demand disclosure of foreign accounts with aggregate balances over $10,000 at any point during the year (penalties can reach 50% of account balances). Cryptocurrency transactions require Form 1040 disclosure regardless of transaction amounts since the IRS classifies digital assets as property subject to capital gains rules.
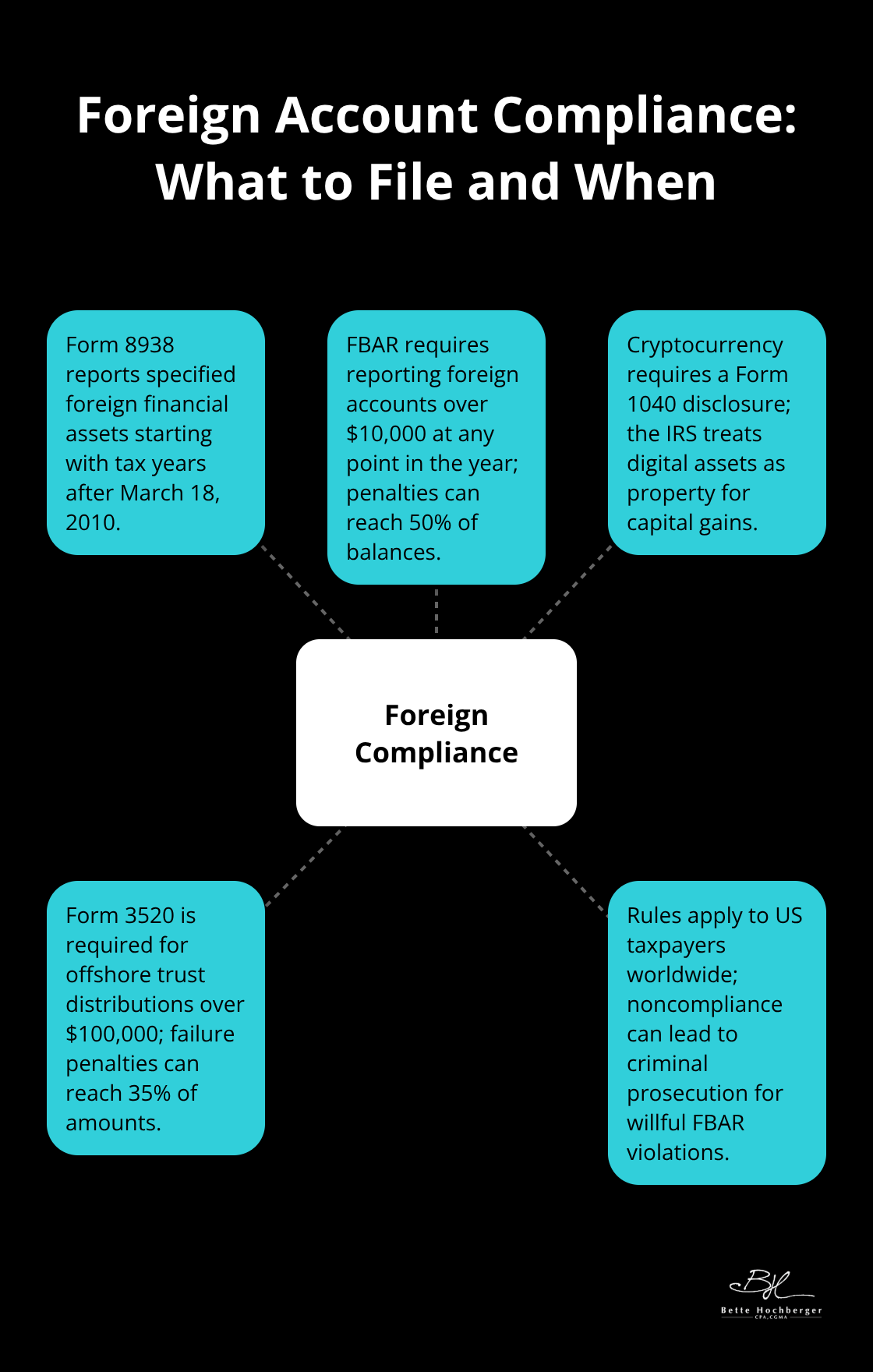
Offshore trust beneficiaries must file Form 3520 when they receive distributions that exceed $100,000, with failure penalties that reach 35% of distribution amounts. These requirements apply to US taxpayers worldwide, which makes compliance essential for avoiding criminal prosecution under willful FBAR violations.
Final Thoughts
Effective tax avoidance demands year-round attention rather than rushed decisions before April deadlines. The IRS processes over 160 million individual returns annually, and taxpayers who plan consistently throughout the year achieve better results than those who wait. Professional guidance becomes necessary when you face complex situations like international income, business transitions, or substantial asset sales.
We at Bette Hochberger, CPA, CGMA work with clients to develop tax strategies that reduce liabilities while maintaining complete compliance. Our professional tax services focus on legitimate deductions, optimal business structures, and strategic income timing. Tax laws evolve constantly, and positions that worked previously may create audit risks today.
Compliant tax planning protects against expensive audits, criminal penalties, and reputation damage that can devastate businesses and personal wealth. Clients who invest in professional tax advice typically save more than advisory fees while building long-term financial security. The difference between legal tax avoidance and criminal evasion often lies in proper documentation and expert oversight (which makes professional guidance a smart investment).