Self-employed individuals often overlook a valuable tax benefit: the self-employed health insurance deduction. This deduction can significantly reduce your taxable income, potentially saving you thousands of dollars each year.
At our firm, we’ve created this comprehensive guide to help you understand, calculate, and maximize this important deduction. Whether you’re a seasoned entrepreneur or just starting your self-employment journey, this post will provide you with the knowledge you need to make informed decisions about your health insurance and taxes.
Understanding the Self-Employed Health Insurance Deduction
What Is the Self-Employed Health Insurance Deduction?
The self-employed health insurance deduction allows eligible individuals to deduct premiums that they pay for medical, dental and qualifying long-term care insurance coverage from their taxable income. This tax benefit applies to health insurance costs for the self-employed person, their spouse, dependents, and children under 27 years old at the end of the tax year.
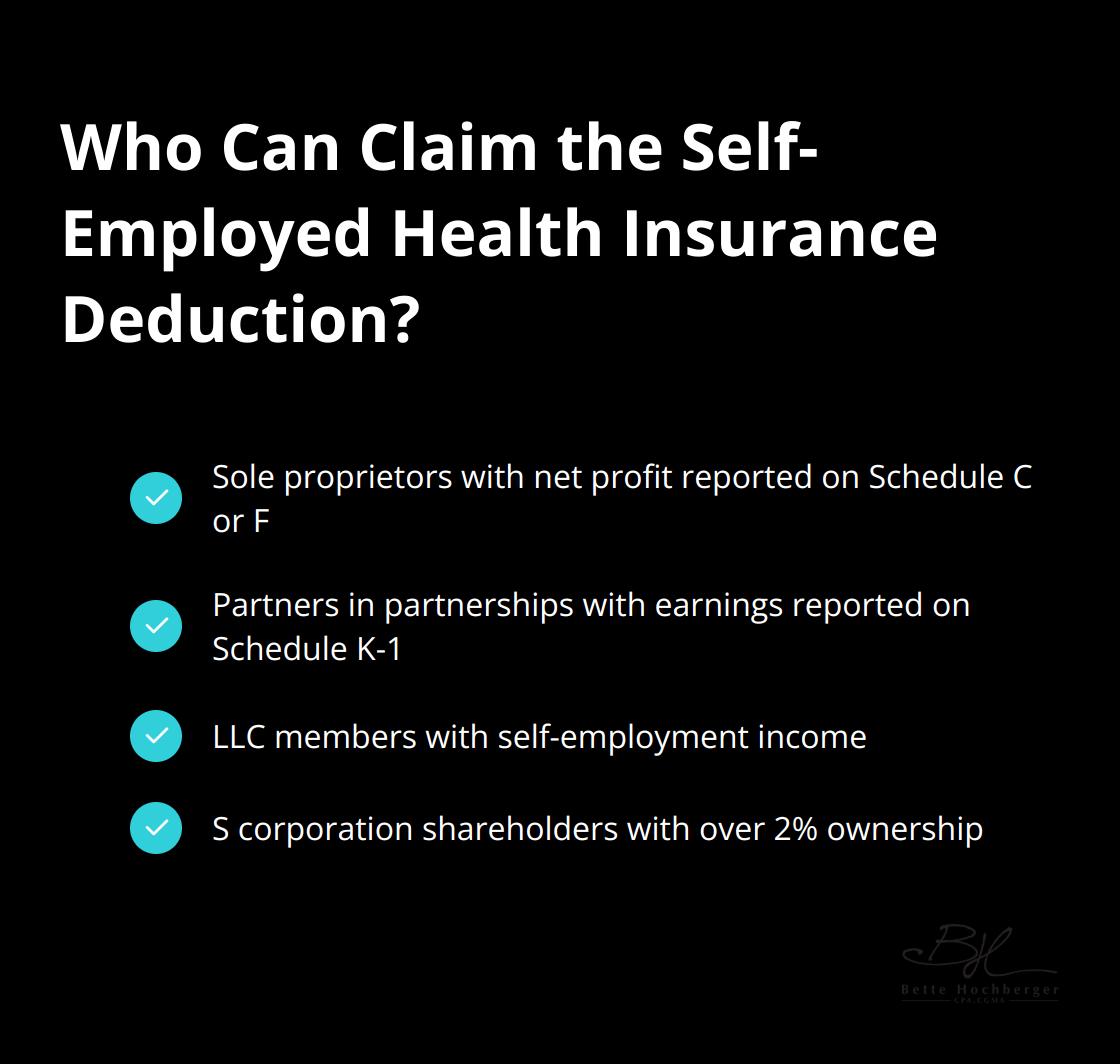
Eligibility Criteria
To qualify for this deduction, you must be self-employed with a net profit reported on Schedule C or Schedule F, or have earnings reported on Schedule K-1 (Form 1065). This includes:
- Sole proprietors
- Partners in partnerships
- LLC members
- S corporation shareholders with over 2% ownership
You can only claim the deduction if your business is profitable. A business loss in the tax year disqualifies you from taking advantage of this deduction.
Eligible Health Insurance Plans
The self-employed health insurance deduction covers a wide range of health insurance plans:
- Medical insurance
- Dental insurance
- Vision insurance
- Long-term care insurance
For long-term care insurance, the IRS sets deduction limits based on age. The eligible premium limits are:
- Age 40 or under: $470
- Age 41 to 50: $880
- Age 51 to 60: $1,760
- Age 61 to 70: $4,710
- Age 71 and over: $5,880
Limitations and Exceptions
While valuable, the self-employed health insurance deduction has limitations. You cannot claim this deduction if you or your spouse have access to employer-sponsored health coverage. The IRS applies this rule on a month-to-month basis, allowing partial deductions for periods without employer coverage.
Additionally, the deduction amount cannot exceed your business’s net profit. If your health insurance premiums are higher than your net profit, you can only deduct up to the amount of your net profit.
It’s essential to keep detailed records of your health insurance payments. These records will help you calculate your deduction accurately and prove invaluable in case of an IRS audit.
Claiming the Deduction
To claim the self-employed health insurance deduction, use Form 7206 to calculate the deduction amount. This form requires you to input your total premiums and net profit figures. Once calculated, report the deduction amount on Schedule 1 of Form 1040.
You cannot claim health insurance premiums on Schedule C as a business expense. However, if you pay premiums for your employees, you can deduct those as employee benefits.
Now that we’ve covered the basics of the self-employed health insurance deduction, let’s move on to the next section, where we’ll explore how to calculate this deduction accurately.
How to Calculate Your Self-Employed Health Insurance Deduction
Gather Necessary Information
The calculation of your self-employed health insurance deduction starts with collecting all relevant data. You need to compile your total health insurance premiums paid for the year, your net profit from self-employment, and any wages from an S corporation (if applicable). Sole proprietors should refer to Schedule C (Form 1040) or Schedule F (Form 1040), while partners should consult Schedule K-1 (Form 1065).
Determine Eligible Premium Amount
The next step involves identifying the amount of health insurance premiums eligible for deduction. This includes premiums paid for medical, dental, and long-term care insurance for you, your spouse, and your dependents. The IRS sets age-based limits on deductible premiums for long-term care insurance.
Calculate the Deduction
Form 7206 is the tool you’ll use to calculate your deduction. This form helps you determine any amount of the self-employed health insurance deduction you may be able to report on Schedule 1 (Form 1040), line 17. Your deduction cannot exceed your business’s net profit.

Handle Multiple Income Sources
For those with multiple sources of self-employment income, you must allocate your health insurance premiums among these sources. The IRS allows you to choose your allocation method, but it must be reasonable and consistent. A common approach allocates based on the percentage of total self-employment income each source represents.
S corporation shareholders who own more than 2% of the corporation’s stock follow a slightly different process. The corporation can pay your health insurance premiums and report them as wages on your W-2. You can then deduct these premiums on your personal tax return.
Avoid Common Mistakes
Several pitfalls can trip up self-employed individuals when calculating their health insurance deduction. One frequent error is the attempt to deduct premiums for months when you or your spouse had access to an employer-sponsored health plan. The IRS disallows deductions for these months, even if you didn’t enroll in the employer’s plan.
Another mistake is the failure to adjust your deduction if you’re claiming a premium tax credit through the Health Insurance Marketplace. Premium tax credits cover the majority of the cost of Marketplace coverage for the average enrollee, making coverage much more affordable. You must reduce your deduction by the amount of any advance premium tax credit you received.
Detailed record-keeping of all premium payments is essential. These records will prove invaluable in the event of an IRS audit to substantiate your deduction claim.
The calculation of your self-employed health insurance deduction can be complex, especially with multiple income sources or unique circumstances. While this guide provides a general overview, tax laws can change, and individual situations vary. For personalized advice tailored to your specific situation, we at Bette Hochberger, CPA, CGMA are here to help. Our expertise in tax planning and strategies can ensure you maximize your deductions while staying compliant with IRS regulations. Now, let’s explore strategies to optimize your self-employed health insurance deduction in the next section.
How to Maximize Your Self-Employed Health Insurance Deduction
Optimize Premium Payment Timing
You can increase your deduction by prepaying your January premium in December. This strategy allows you to claim 13 months of premiums in a single tax year, potentially boosting your deduction. However, this method works best if your current year’s income exceeds your expected income for the following year.
Leverage Health Savings Accounts
Combining a high-deductible health plan (HDHP) with a Health Savings Account (HSA) provides additional tax benefits. For 2025, you can contribute up to $4,300 if you are covered by a high-deductible health plan just for yourself, or $8,550 if you have coverage for your family. HSA contributions offer a triple tax advantage: they’re tax-deductible, grow tax-free, and can be withdrawn tax-free for qualified medical expenses.
Coordinate with Other Tax Benefits
You must coordinate your self-employed health insurance deduction with other available tax benefits. If you qualify for premium tax credits through the Health Insurance Marketplace, adjust your deduction accordingly. The U.S. Department of Health & Human Services reports that in 2024, the number of people with Marketplace coverage grew from 16.4 million in 2023 to 21.4 million.

Plan for Future Tax Years
Look ahead to maximize your deduction. Consider your projected income and potential changes in your business structure. If you anticipate a significant income increase, explore options for more comprehensive coverage. Higher premiums could be offset by a larger deduction.
Stay informed about legislative changes. The American Rescue Plan enhanced the Affordable Care Act’s premium tax credits, making them larger and more accessible through 2025. Such changes can impact your overall tax strategy and the value of your health insurance deduction.
Seek Professional Advice
Tax professionals can provide personalized advice based on your specific situation. They help navigate the complexities of self-employed health insurance deductions and related tax issues. While many options exist, firms specializing in tax planning for self-employed individuals (such as Bette Hochberger, CPA, CGMA) can offer tailored strategies to maximize your deductions.
Final Thoughts
The self-employed health insurance deduction offers entrepreneurs a powerful tool to reduce taxable income and manage healthcare costs. This deduction allows eligible individuals to subtract premiums for medical, dental, and long-term care insurance from their taxable income. Proper understanding of eligibility criteria, accurate calculation, and strategic planning maximize the benefits of this deduction.
Accurate record-keeping proves essential when claiming the self-employed health insurance deduction. Detailed documentation of all premium payments supports your deduction claim during tax preparation and potential IRS audits. Tax laws can change, and individual situations vary, so personalized advice becomes valuable for optimal tax strategies.
We at Bette Hochberger, CPA, CGMA specialize in tax planning for self-employed individuals and small businesses. Our team can help you navigate the complexities of the self-employed health insurance deduction and develop a comprehensive tax strategy tailored to your needs. Professional guidance allows you to focus on growing your business while we handle your tax situation.










